n8n Security Alert: New Severe Flaws and Essential Updates

Introduction: n8n Security Alert
n8n, the popular open-source workflow automation platform, faces a major security crisis with newly disclosed severe vulnerabilities that demand immediate action from users worldwide. These flaws, including critical remote code execution risks, underscore the urgent need for patches and hardened configurations to safeguard automation pipelines.
Table of Contents
Vulnerability Overview
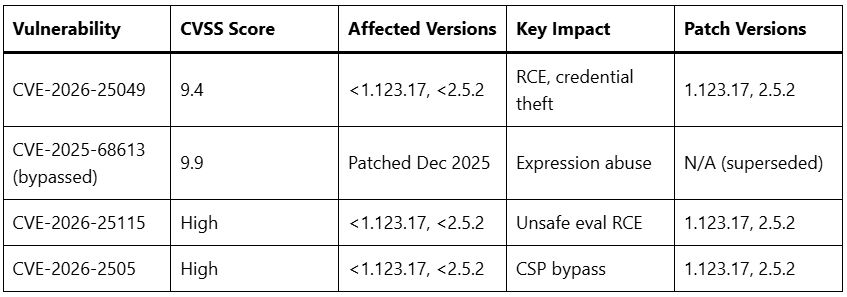
Recent disclosures reveal CVE-2026-25049 as a critical flaw with a CVSS score of 9.4, stemming from inadequate sanitization in n8n’s expression evaluation system. This vulnerability bypasses safeguards implemented for the prior CVE-2025-68613 (CVSS 9.9), allowing authenticated users with workflow creation or editing permissions to execute arbitrary system commands on the host server. Exploitation requires minimal effort: an attacker crafts malicious expressions in workflow parameters, triggering unintended command execution that exposes sensitive data like API keys, OAuth tokens, database passwords, and filesystem access.
Additional related flaws compound the threat. CVE-2026-25115 enables unsafe workflow expression evaluation leading to remote code execution, while CVE-2026-2505 involves improper Content Security Policy enforcement, further weakening defenses. These affect n8n versions before 1.123.17 and 2.5.2, with public proofs-of-concept (PoCs) now circulating that demonstrate low-complexity attacks. When combined with n8n’s webhook nodes, attackers can expose malicious payloads publicly, amplifying risks for AI-driven workflows connecting cloud services, LLMs, and internal systems.
Exploitation Mechanics
The core issue lies in n8n’s handling of user-supplied expressions within workflows. Despite TypeScript type checks, runtime validation fails against crafted inputs that evade sanitization, smuggling shell commands onto the host OS. For instance, an authenticated adversary modifies a node parameter with a payload like a disguised command injection, executing during workflow runtime and granting shell access without authentication escalation.
Pillar Security highlights how webhook integration escalates this: a public webhook triggers the vulnerable workflow, enabling unauthenticated remote access if improperly configured. Real-world impacts include credential theft from connected services (e.g., OpenAI API keys, AWS credentials), lateral movement to cloud accounts, AI workflow hijacking, and full server compromise. Cybersecurity firms like Endor Labs emphasize that single-layer protections prove insufficient; multiple runtime checks are essential for untrusted inputs.
This follows a pattern of n8n woes. Just weeks prior, “ni8mare” (another unauthenticated RCE) exposed ~100,000 instances, and earlier flaws like CVE-2025-68668 and sandbox escapes (JFrog-reported) provided “skeleton keys” to corporate infrastructure. n8n maintainers acknowledged these in a February 6, 2026, security bulletin, confirming patches but urging vigilance.
Affected Versions and Scope
Vulnerabilities impact n8n self-hosted instances from version 1.0.0 up to but excluding 1.123.17 (legacy branch) and 2.5.2 (main branch), including popular ranges like 1.65-1.120.4. Cloud-hosted n8n (n8n.cloud) remains unaffected due to isolated environments, but on-premises deployments common for enterprises handling sensitive automations are at high risk.
Global adoption amplifies exposure: n8n powers thousands of workflows stitching CRM, sales data, IAM, and AI tools across organizations. In regions like India, where automation tools integrate with growing cloud ecosystems, unpatched instances risk data breaches amid rising cyber threats. Public PoCs lower the bar for script kiddies, with advisories from CISA-like bodies (e.g., Singapore’s CSA) flagging it as critical.
Mitigation Strategies
Immediate upgrades to n8n 1.123.17 or 2.5.2 resolve all disclosed flaws by enhancing expression sanitization, adding runtime validations, and tightening CSP rules. For self-hosted setups, deploy in hardened environments: run as a non-root user, isolate via Docker with limited privileges, firewall webhooks, and enable execution isolation modes.
Restrict workflow permissions rigorously, limit creation/editing to trusted admins only, audit user roles, and monitor for anomalous expressions via logs. Implement network segmentation to block lateral movement, rotate all exposed credentials (API keys, tokens), and scan workflows for PoC patterns post-incident. Tools like workflow diffing and SIEM integration help detect changes; for AI-heavy pipelines, add output validation to prevent poisoned responses.
Organizations should inventory n8n instances, prioritize patching based on exposure (e.g., public webhooks), and conduct penetration tests. n8n’s community forum stresses reviewing access controls, as even authenticated access suffices for compromise.
Broader Implications for Automation
These flaws spotlight risks in workflow platforms like n8n, Zapier alternatives, and emerging AI orchestrators, where “low-code” convenience meets high-stakes integrations. Attackers increasingly target them as “skeleton keys” to enterprises, blending automation with AI to exfiltrate data undetected. Recent trends show a 30% rise in supply-chain attacks on DevOps tools, with RCE flaws enabling persistent footholds.
For developers and IT teams, this reinforces zero-trust principles: treat all inputs as hostile, layer defenses beyond static analysis, and prioritize runtime security. n8n’s rapid patching trajectory multiple fixes in 2026, demonstrates responsiveness, but users must match it with proactive hygiene. In regulated sectors (finance, healthcare), compliance audits now flag such tools, pushing air-gapped or managed alternatives.
Essential Updates and Best Practices
Beyond patching, adopt these trending practices gaining traction in 2026 cybersecurity discourse:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Enforce role-based access control (RBAC) granularly; use n8n’s enterprise features for audit trails.
- Secrets Management: Shift API keys to vaults like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager, avoiding plaintext storage.
- Monitoring and Response: Integrate with tools like Falco for runtime anomaly detection in containers; set alerts for command spawns.
- Regular Audits: Schedule bi-weekly workflow reviews, leveraging n8n’s API for bulk scans of expressions.
- Backup and Recovery: Maintain immutable snapshots of workflows and configs; test restores quarterly.
n8n’s maintainers continue releasing advisories, with February 2026 updates addressing only publicly known issues; one PoC circulates widely. Staying current via the community forum and GitHub advisories remains crucial amid this evolving threat landscape.
The Future-Proofing Workflows
As automation evolves with Agentforce-like AI agents and Slack integrations, expect heightened scrutiny on expression engines and sandboxing. Emerging standards like SLSA (Supply-chain Levels for Software Artifacts) will benchmark tools like n8n, favoring those with verifiable runtime isolation. Users integrating n8n with Salesforce Flows or n8n’s own AI nodes should validate inputs doubly, treating automations as execution environments rivaling traditional apps.

