The Complete Guide to Successful Salesforce Implementation

Introduction: Guide to Successful Salesforce Implementation
Salesforce stands as the top Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform globally, helping businesses enhance their sales, marketing, customer support, and operations. Yet, to implement Salesforce effectively, businesses must focus on careful planning, execution, and continuous improvement.
This comprehensive guide covers every step of a successful Salesforce implementation, from pre-planning to post-deployment best practices. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, this guide will help you maximize ROI and ensure a smooth transition.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Salesforce Implementation
What is Salesforce implementation?
Salesforce implementation refers to the process of deploying Salesforce CRM within an organization, configuring it to meet business needs, migrating data, training users, and ensuring adoption.
Why is Proper Implementation Important?
- Enhances efficiency – Automates workflows and reduces manual tasks.
- Improves data management – Centralizes customer data for better insights.
- Boosts sales & customer service – Provides tools for better engagement.
- Scales with growth – Adapts to changing business needs.
Types of Salesforce Implementations
- Sales Cloud – For sales automation and pipeline management.
- Service Cloud – For customer support and case management.
- Marketing Cloud – For email marketing and campaign automation.
- Commerce Cloud – For e-commerce and omnichannel sales.
- Community Cloud – For partner and customer portals.
2. Pre-Implementation Planning
A. Define Business Objectives
- Identify key pain points (e.g., inefficient sales tracking, poor customer data management).
- Set measurable goals (e.g., increase lead conversion by 20%, reduce response time by 30%).
B. Assemble the Right Team
- Executive Sponsor – Ensures leadership buy-in.
- Project Manager – Oversees the implementation.
- Salesforce Admin/Consultant – Handles configuration and customization.
- IT Team – Manages integrations and security.
- End-User Representatives – Provide feedback on usability.
C. Choose the Right Salesforce Edition
- Essentials – For small businesses (up to 10 users).
- Professional – For growing teams with basic CRM needs.
- Enterprise – For advanced customization and automation.
- Unlimited – For large enterprises with complex requirements.
D. Assess Data Readiness
- Data Audit – Identify existing data sources (Excel, legacy CRM).
- Data Cleansing – Remove duplicates and outdated records.
- Data Mapping – Define how data will migrate to Salesforce.
E. Develop a Project Timeline
- Phase 1: Planning & Discovery (2-4 weeks).
- Phase 2: Configuration & Customization (4-8 weeks).
- Phase 3: Data Migration (1-2 weeks).
- Phase 4: User Training (1-2 weeks).
- Phase 5: Go-Live & Post-Implementation Support (Ongoing).
3. Salesforce Configuration & Customization
A. Setting Up Salesforce Org
- Company Profile – Configure business hours, currencies, and language settings.
- User Roles & Profiles – Define access permissions.
- Security Settings – Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and IP restrictions.
B. Customizing Objects & Fields
- Standard Objects (Accounts, Contacts, Leads, Opportunities).
- Custom Objects – Create new entities (e.g., projects, events).
- Custom Fields – Add unique data points (e.g., Customer Segment, Contract Type).
C. Automating Workflows
- Process Builder – Automate approvals, notifications, and record updates.
- Flow Builder – Design complex business processes.
- Approval Processes – Streamline approval chains.
D. Integrating Third-Party Apps
- Marketing Automation (HubSpot, Marketo).
- ERP Systems (SAP, Oracle).
- Communication Tools (Slack, Outlook).
- Payment Gateways (Stripe, PayPal).
E. Building Reports & Dashboards
- Sales Pipeline Reports – Track deals by stage.
- Customer Service Metrics – Monitor case resolution times.
- Executive Dashboards – High-level performance insights.
4. Data Migration Strategies
A. Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) Process
- Extract – Pull data from legacy systems (CSV, SQL, APIs).
- Transform – Clean, deduplicate, and reformat data.
- Load – Import into Salesforce using Data Loader or third-party tools.
B. Best Practices for Data Migration
- Start with a Test Migration – Validate data before full import.
- Use Unique IDs – Prevent duplicate records.
- Schedule Off-Peak Migration – Minimize disruption.
C. Tools for Data Migration
- Salesforce Data Loader – For bulk imports/exports.
- Informatica Cloud – For complex ETL processes.
- Jitterbit – For API-based integrations.
5. User Training & Adoption Strategies
A. Role-Based Training Programs
- Sales Teams – Lead management, opportunity tracking.
- Customer Support – Case Management, Knowledge Base.
- Marketing Teams – Campaign tracking, lead nurturing.
B. Training Methods
- In-Person Workshops – Hands-on sessions.
- Webinars & Video Tutorials – On-demand learning.
- Sandbox Environment – Safe space for practice.
C. Driving User Adoption
- Gamification – Reward top users with badges.
- Feedback Loops – Collect and address user concerns.
- Ongoing Support – Provide a help desk or super-users.
6. Go-Live & Post-Implementation Support
A. Go-Live Checklist
- Final data validation.
- User access permissions confirmed.
- Backups and rollback plans are in place.
B. Monitoring Performance
- Track system usage with Salesforce Adoption Dashboards.
- Identify bottlenecks (e.g., slow reports, automation errors).
C. Continuous Improvement
- Quarterly Reviews – Assess KPIs and adjust configurations.
- Salesforce Releases – Stay updated with new features (3x yearly).
- User Feedback Surveys – Improve UX based on input.
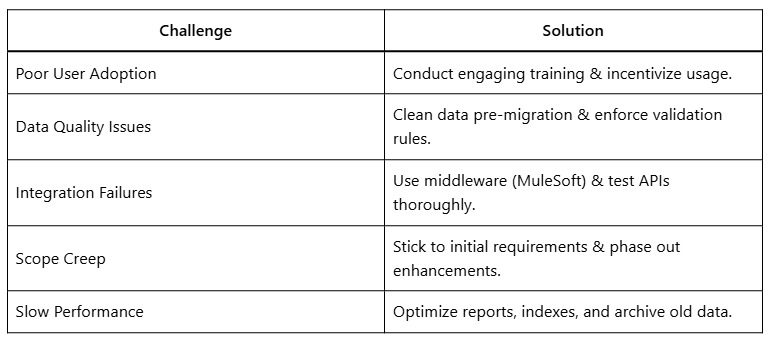
7. Common Salesforce Implementation Challenges & Solutions
8. Measuring Salesforce Implementation Success
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Sales Metrics – Win rate, average deal size, sales cycle length.
- Service Metrics – First-call resolution, customer satisfaction (CSAT).
- Adoption Rate – Active users, login frequency.
ROI Calculation
- Compare pre- and post-Salesforce efficiency gains.
- Factor in cost savings (reduced manual work, fewer software licenses).
9. The Future-Proofing Your Salesforce Implementation
1. AI & Predictive Analytics
Einstein AI to gain actionable insights, automate workflows, and enhance decision-making. Predictive analytics can forecast trends, improve customer engagement, and optimize operations, keeping your business ahead of the competition.
2. Mobile Optimization
With an increasing reliance on remote work, ensure Salesforce Mobile is fully utilized. A seamless mobile experience boosts productivity, enables real-time data access, and improves user adoption across teams, regardless of location.
3. Scalability
Design your Salesforce architecture to accommodate growth, including mergers, acquisitions, and global expansion. Flexible data models, multi-currency support, and scalable integrations ensure smooth transitions as your business evolves.
My Takeaway:
Implementing Salesforce successfully requires careful planning, clear goals, and strong execution. Start by defining your business objectives and involving key stakeholders early. Choose the right Salesforce edition and customize it to fit your workflows. Ensure proper data migration, user training, and ongoing support to maximize adoption. Regularly review performance and leverage Salesforce’s analytics for continuous improvement.

