How to Build Dynamic Portals with Real-Time Salesforce Integration

Introduction
In the era of digital transformation, businesses require agile, responsive, and data-driven customer and employee portals that seamlessly integrate with backend systems like Salesforce. Dynamic portals, unlike static ones, adapt in real-time based on user interactions, permissions, and live data changes. Integrating these portals with Salesforce in real-time ensures that users always have access to the latest information, enabling faster decision-making, improved customer service, and streamlined operations.
This in-depth guide explores the architecture, technologies, and step-by-step process of building dynamic portals with real-time Salesforce integration. We will cover key concepts, best practices, challenges, and solutions to help developers and businesses create powerful, interactive portals.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Dynamic Portals With Real-Time Salesforce Integration
1.1 What Are Dynamic Portals?
Dynamic portals are web-based platforms that dynamically render content based on:
- User roles (e.g., customers, employees, partners).
- Real-time data changes (e.g., order status updates, case resolutions).
- Personalization rules (e.g., preferred language, dashboard widgets).
Unlike traditional static portals, dynamic portals:
- Automatically update without requiring manual refreshes.
- Support interactive elements like live chat, notifications, and dashboards.
- Improve user experience by reducing latency and providing instant feedback.
1.2 Why Real-Time Salesforce Integration?
Salesforce is the world’s leading CRM platform, and integrating it with portals in real-time offers several advantages:
- Instant Data Synchronization: Eliminates delays in case updates, lead assignments, and order tracking.
- Automated Workflows: Triggers actions (e.g., sending notifications when a case status changes).
- Self-Service Capabilities: Allows customers and employees to access and update records without manual intervention.
1.3 Common Use Cases
- Customer Self-Service Portals: View orders, submit support tickets, and track case status.
- Partner Portals: Access leads, commissions, and collaborative deal management.
- Employee Portals: Submit HR requests, view approvals, and access company documents.
2. Key Components of a Dynamic Portal with Salesforce Integration
2.1 Frontend Technologies
- React, Angular, or Vue.js: Modern JavaScript frameworks for building responsive, interactive UIs.
- Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS: For styling and ensuring mobile responsiveness.
- WebSockets or Server-Sent Events (SSE): Enables real-time data streaming.
2.2 Backend Technologies
- Node.js, Python (Django/Flask), or Java (Spring Boot): Handles business logic and API integrations.
- Express.js or FastAPI: For building RESTful APIs.
- GraphQL: An alternative to REST for flexible querying of Salesforce data.
2.3 Salesforce Integration Methods
- Salesforce REST API – Standard HTTP-based API for CRUD operations.
- Salesforce SOAP API – Useful for complex enterprise integrations.
- Salesforce Streaming API – Provides real-time notifications via PushTopics and Platform Events.
- Salesforce Connect – Allows external systems to query Salesforce data in real-time.
- Middleware (MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, Zapier) – Useful for complex integrations requiring transformation logic.
2.4 Authentication & Security
- OAuth 2.0 / OpenID Connect: Secure authentication between the portal and Salesforce.
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens): For stateless session management.
- CORS & CSRF Protection: Prevents cross-origin and cross-site request forgery attacks.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Dynamic Portal with Real-Time Salesforce Integration
3.1 Step 1: Define Business Requirements
- Identify user roles (e.g., customers, agents, admins).
- Determine which Salesforce objects (e.g., cases, accounts, opportunities) need integration.
- Decide on real-time needs (e.g., live notifications, auto-refreshing dashboards).
3.2 Step 2: Choose the Right Technology Stack
- Frontend: React (for dynamic UI) + Material-UI (for styling).
- Backend: Node.js + Express (for API handling).
- Database: PostgreSQL (optional, for caching frequently accessed data).
- Integration: Salesforce REST API + Streaming API.
3.3 Step 3: Configure Salesforce for Integration
1. Enable API Access:
- Navigate to Setup > API and ensure API access is enabled.
2. Create a Connected App:
- Go to Setup > App Manager > New Connected App.
- Configure OAuth settings (callback URL, scopes like api, refresh_token).
3. Set Up Real-Time Events:
Option 1: PushTopic (for standard objects like Cases):
PushTopic pushTopic = new PushTopic();
pushTopic.Name = ‘CaseUpdates’;
pushTopic.Query = ‘SELECT Id, Subject, Status FROM Case’;
pushTopic.ApiVersion = 50.0;
pushTopic.NotifyForOperationCreate = true;
pushTopic.NotifyForOperationUpdate = true;
insert pushTopic;
Option 2: Platform Event (for custom real-time triggers):
- Create a Platform Event in Salesforce Setup.
- Define fields (e.g.,
CaseId,NewStatus).
3.4 Step 4: Develop the Backend (Node.js Example)
const express = require(‘express’);
const axios = require(‘axios’);
const { jsforce } = require(‘jsforce’);
const jwt = require(‘jsonwebtoken’);
const app = express();
app.use(express.json());
// OAuth 2.0 Authentication with Salesforce
app.post(‘/auth/salesforce’, async (req, res) => {
const { code } = req.body;
const authUrl = ‘https://login.salesforce.com/services/oauth2/token’;
try {
const response = await axios.post(authUrl, new URLSearchParams({
grant_type: ‘authorization_code’,
client_id: process.env.SF_CLIENT_ID,
client_secret: process.env.SF_CLIENT_SECRET,
redirect_uri: process.env.SF_CALLBACK_URL,
code,
}));
const { access_token, instance_url } = response.data;
const conn = new jsforce.Connection({ instanceUrl: instance_url, accessToken: access_token });
// Fetch user details
const user = await conn.identity();
const token = jwt.sign({ user }, process.env.JWT_SECRET, { expiresIn: '1h' });
res.json({ token, instanceUrl: instance_url });} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: ‘Authentication failed’ });
}
});
// Real-Time Subscription (Salesforce Streaming API)
app.get(‘/api/stream’, (req, res) => {
const conn = new jsforce.Connection({
accessToken: req.headers.authorization.split(‘ ‘)[1],
instanceUrl: req.headers[‘instance-url’],
});
const topic = ‘/topic/CaseUpdates’;
conn.streaming.topic(topic).subscribe((message) => {
res.write(data: ${JSON.stringify(message)}\n\n);
});
res.setHeader(‘Content-Type’, ‘text/event-stream’);
res.setHeader(‘Cache-Control’, ‘no-cache’);
res.setHeader(‘Connection’, ‘keep-alive’);
});
// Fetch Cases (REST API Example)
app.get(‘/api/cases’, async (req, res) => {
const conn = new jsforce.Connection({
accessToken: req.headers.authorization.split(‘ ‘)[1],
instanceUrl: req.headers[‘instance-url’],
});
try {
const cases = await conn.query(‘SELECT Id, Subject, Status FROM Case’);
res.json(cases.records);
} catch (error) {
res.status(500).json({ error: ‘Failed to fetch cases’ });
}
});
app.listen(3000, () => console.log(‘Server running on port 3000’));
3.5 Step 5: Build the Frontend (React Example)
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import axios from 'axios';
const CaseDashboard = () => {
const [cases, setCases] = useState([]);
const [eventSource, setEventSource] = useState(null);
// Fetch initial cases
useEffect(() => {
const fetchCases = async () => {
const token = localStorage.getItem('token');
const instanceUrl = localStorage.getItem('instanceUrl');
const response = await axios.get('/api/cases', {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${token}`,
'Instance-Url': instanceUrl,
},
});
setCases(response.data);
};
fetchCases();
// Set up real-time updates via SSE
const source = new EventSource('/api/stream');
source.onmessage = (e) => {
const updatedCase = JSON.parse(e.data);
setCases(prevCases =>
prevCases.map(c => c.Id === updatedCase.Id ? updatedCase : c)
);
};
setEventSource(source);
return () => source.close();
}, []);
return (
<div>
<h1>Case Management Dashboard</h1>
<ul>
{cases.map(c => (
<li key={c.Id}>
<strong>{c.Subject}</strong> - {c.Status}
</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
);
};
export default CaseDashboard;
3.6 Step 6: Deploy and Monitor
1. Hosting Options:
- Cloud Platforms: AWS (EC2, Lambda), Azure, Heroku.
- Containerization: Docker + Kubernetes for scalability.
2. CI/CD Pipeline:
- GitHub Actions, Jenkins, or CircleCI for automated deployments.
3. Monitoring & Logging:
- Salesforce Event Monitoring: Track API usage.
- New Relic/Datadog: Monitor portal performance.
4. Best Practices for Real-Time Salesforce Portal Integration
4.1 Optimize API Calls
- Use bulk APIs for large datasets.
- Implement client-side caching to reduce redundant requests.
4.2 Handle Errors Gracefully
- Implement retry mechanisms for failed API calls.
- Use circuit breakers to prevent cascading failures.
4.3 Secure the Integration
- Enforce HTTPS for all communications.
- Validate OAuth scopes to restrict unnecessary permissions.
- Use rate limiting to prevent API abuse.
4.4 Ensure Scalability
- Use load balancers for high-traffic portals.
- Cache frequently accessed data to reduce Salesforce API load.
5. Common Challenges & Solutions
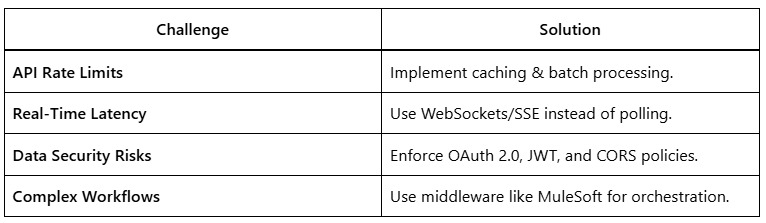
6. Conclusion
Building a dynamic portal with real-time Salesforce integration requires careful planning, the right technology stack, and adherence to best practices. By leveraging modern frontend frameworks, robust backend services, and Salesforce’s powerful APIs, businesses can create seamless, interactive experiences that enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.

