Building a Robust Observability Framework for Salesforce Orgs

Introduction
In today’s digital-first business landscape, Salesforce serves as the backbone for customer relationship management (CRM), sales automation, marketing, and service operations. As organizations scale their Salesforce usage, ensuring system reliability, performance, and security becomes critical. A robust observability framework is essential to proactively monitor, debug, and optimize Salesforce orgs.
Observability goes beyond traditional monitoring it provides deep insights into system behavior by collecting and analyzing logs, metrics, and traces. For Salesforce, observability helps detect issues before they impact users, improves troubleshooting efficiency, and enhances overall system health.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Observability in Salesforce
What is observability?
Observability refers to the ability to infer the internal state of a system based on its external outputs. Unlike monitoring, which tracks predefined metrics, observability helps answer unknown unknowns unexpected issues that arise in complex systems.
Why is Observability Critical for Salesforce?
Salesforce is a multi-tenant, cloud-based platform with dynamic workloads, integrations, and customizations. Without proper observability, organizations face:
- Performance bottlenecks (slow reports, dashboard delays)
- Integration failures (API timeouts, authentication errors)
- Security risks (unauthorized access, data leaks)
- User experience degradation (unresponsive UI, errors)
2. Key Pillars of Observability: Logs, Metrics, and Traces
A. Logs
Logs provide a record of events within Salesforce, including:
- Apex execution logs (debug statements, errors)
- API call logs (REST/SOAP requests)
- Login history & security logs (audit trails)
- Event monitoring logs (user activity, data access)
Best Practices for Log Management:
✔ Enable debug logs for developers (but limit retention due to storage constraints).
✔ Use Event Monitoring (paid Salesforce feature) for granular tracking.
✔ Forward logs to a SIEM (e.g., Splunk, Datadog) for long-term retention.
B. Metrics
Metrics are quantitative measurements of system performance, such as
- API Latency (response times)
- CPU Timeouts (governor limit breaches)
- Storage Utilization (data, file, and Big Object usage)
- User Activity Rates (logins, page views)
Best Practices for Metrics Collection:
✔ Leverage Salesforce Health Check for security & performance benchmarks.
✔ Use custom metrics (via Prometheus or New Relic integrations).
✔ Set up alerts for threshold breaches (e.g., API call limits).
C. Traces
Traces track end-to-end request flows, crucial for debugging:
- Transaction execution paths (Apex → Flow → Integration)
- Distributed tracing (for microservices & external APIs)
Best Practices for Tracing:
✔ Use OpenTelemetry for standardized tracing.
✔ Correlate logs & traces for faster debugging.
3. Tools and Technologies for Salesforce Observability
Native Salesforce Tools
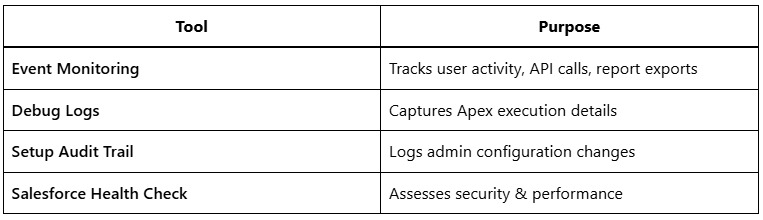
Third-Party Observability Solutions
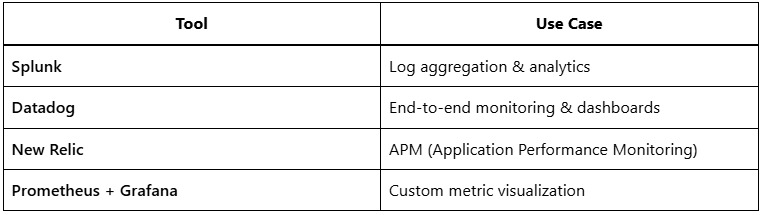
Custom Integrations
- AWS CloudWatch / Azure Monitor (for hybrid cloud setups)
- ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) for log analysis
4. Best Practices for Implementation
Step 1: Define Observability Goals
- What KPIs matter? (e.g., API latency, error rates)
- Who needs access? (DevOps, Security, Business Analysts)
Step 2: Instrument Salesforce for Observability
✔ Enable Event Monitoring (Salesforce Shield or Event Log File).
✔ Configure Log Forwarding (to Splunk or SIEM).
✔ Implement Distributed Tracing (for integrations).
Step 3: Automate Alerts & Dashboards
- Proactive Alerts (e.g., “CPU time exceeded 80%”)
- Real-time Dashboards (e.g., User activity heatmaps)
Step 4: Continuously Optimize
- Review logs/metrics weekly to refine thresholds.
- Conduct incident post-mortems to improve detection.
5. Real-World Use Cases
Case 1: Debugging a Slow Salesforce Report
Issue: Users complain about report timeouts.
Observability Approach:
- Check Apex logs for inefficient SOQL queries.
- Analyze API metrics for excessive data retrieval.
- Solution: Optimize SOQL, add indexes.
Case 2: Detecting Suspicious User Activity
Issue: Unusual login patterns from a foreign IP.
Observability Approach:
- Review Login History logs.
- Trigger automated alerts via Splunk.
- Solution: Enforce MFA, block suspicious IPs.
6. Future Trends in Salesforce Observability
AI-Powered Anomaly Detection (predictive alerts)
Unified Observability Platforms (combining logs, metrics, traces)
Enhanced Salesforce Native Tools (deeper OpenTelemetry support)
My Takeway: Robust Observability Framework
A well-architected observability framework is no longer optional for Salesforce orgs it’s a competitive necessity. By leveraging logs, metrics, and traces, integrating with modern monitoring tools, and following best practices, organizations can ensure peak performance, security, and reliability.

